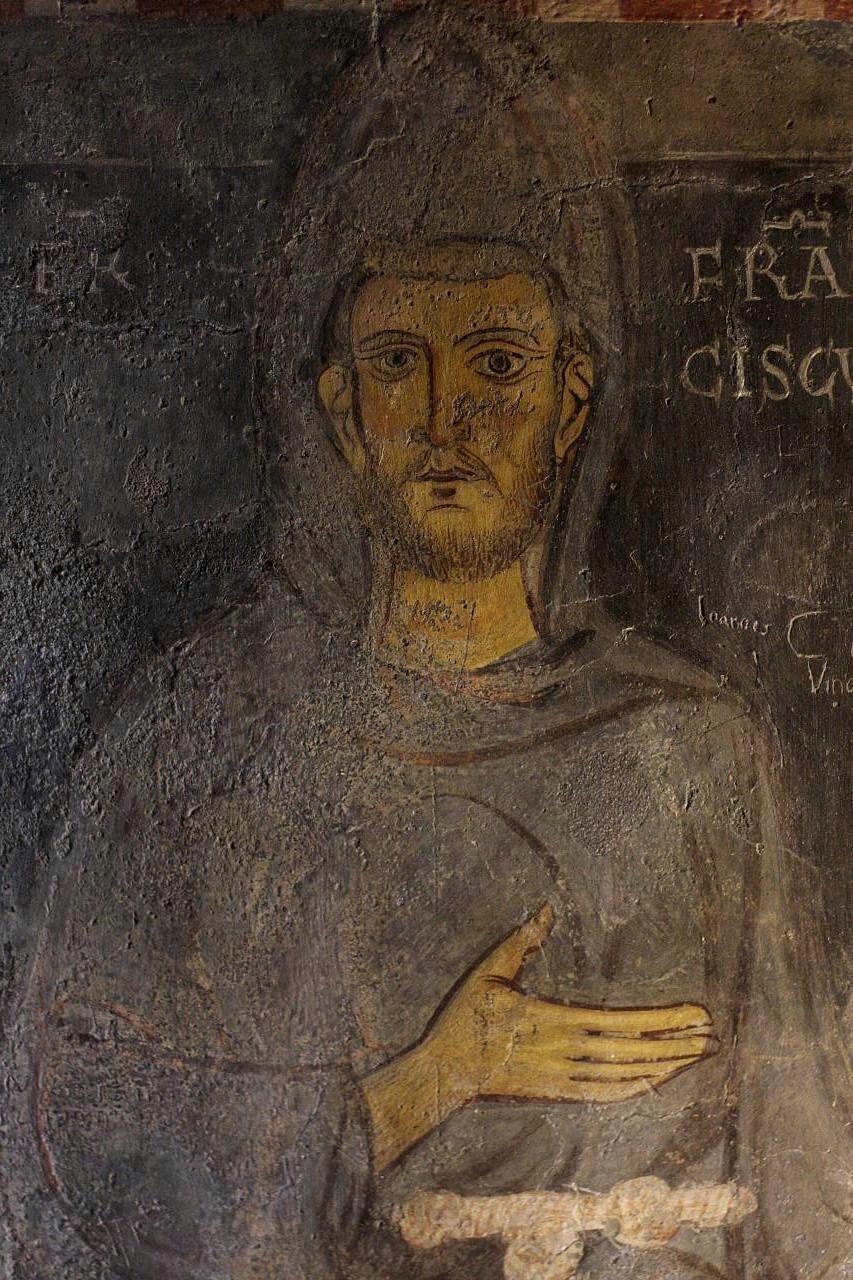
Probably the oldest likeness of Francis that has come down to us is that preserved in the Sacro Speco at Subiaco. It is said that it was painted by a Benedictine monk during the saint’s visit there, which may have been in 1218. The absence of the stigmata, halo, and title of saint in this fresco form its chief claim to be considered a contemporary picture; it is not, however, a real portrait in the modern sense of the word, and we are dependent for the traditional presentment of Francis rather on artists’ ideals, like the Della Robbia statue at the Porziuncola, which is surely the saint’s vera effigies, as no Byzantine so-called portrait can ever be, and the graphic description of Francis given by Celano (Vita Prima, c.lxxxiii). Of less than middle height, we are told, and frail in form, Francis had a long yet cheerful face and soft but strong voice, small brilliant black eyes, dark brown hair, and a sparse beard. His person was in no way imposing, yet there was about the saint a delicacy, grace, and distinction which made him most attractive.
The literary materials for the history of St. Francis are more than usually copious and authentic. There are indeed few if any medieval lives more thoroughly documented. We have in the first place the saint’s own writings. These are not voluminous and were never written with a view to setting forth his ideas systematically, yet they bear the stamp of his personality and are marked by the same unvarying features of his preaching. A few leading thoughts taken “from the words of the Lord” seemed to him all sufficing, and these he repeats again and again, adapting them to the needs of the different persons whom he addresses. Short, simple, and informal, Francis’s writings breathe the unstudied love of the Gospel and enforce the same practical morality, while they abound in allegories and personification and reveal an intimate interweaving of Biblical phraseology. Not all the saint’s writings have come down to us, and not a few of these formerly attributed to him are now with greater likelihood ascribed to others. The extant and authentic opusculaof Francis comprise, besides the rule of the Friars Minor and some fragments of the other Seraphic legislation, several letters, including one addressed “to all the Christians who dwell in the whole world,” a series of spiritual counsels addressed to his disciples, the “Laudes Creaturarum” or “Canticle of the Sun”, and some lesser praises, an Office of the Passion compiled for his own use, and few other orisons which show us Francis even as Celano saw him, “not so much a man’s praying as prayer itself”. In addition to the saint’s writings the sources of the history of Francis include a number of early papal bulls and some other diplomatic documents, as they are called, bearing upon his life and work. Then come the biographies properly so called. These include the lives written 1229-1247 by Thomas of Celano, one of Francis’s followers; a joint narrative of his life compiled by Leo, Rufinus, and Angelus, intimate companions of the saint, in 1246; and the celebrated legend of St. Bonaventure, which appeared about 1263; besides a somewhat more polemic legend called the “Speculum Perfectionis”, attributed to Brother Leo, the sate of which is a matter of controversy. There are also several important thirteenth- century chronicles of the order, like those of Jordan, Eccleston, and Bernard of Besse, and not a few later works, such as the “Chronica XXIV. Generalium” and the “Liber de Conformitate”, which are in some sort a continuation of them. It is upon these works that all the later biographies of Francis’s life are based.
What Does Saint Thomas Say About Immigration?
Recent years have witnessed a truly remarkable upgrowth of interest in the life and work of St. Francis, more especially among non-Catholics, and Assisi has become in consequence the goal of a new race of pilgrims. This interest, for the most part literary and academic, is centered mainly in the study of the primitive documents relating to the saint’s history and the beginnings of the Franciscan Order. Although inaugurated some years earlier, this movement received its greatest impulse from the publication in 1894 of Paul Sabatier’s “Vie de S. François”, a work which was almost simultaneously crowned by the French Academy and place upon the Index. In spite of the author’s entire lack of sympathy with the saint’s religious standpoint, his biography of Francis bespeaks vast erudition, deep research, and rare critical insight, and it has opened up a new era in the study of Franciscan resources. To further this study and International Society of Franciscan Studies was founded at Assisi in 1902, the aim of which is to collect a complete library of works on Franciscan history and to compile a catalog of scattered Franciscan manuscripts; several periodicals, devoted to Franciscan documents and discussions exclusively, have moreover been established in different countries. Although a large literature has grown up around the figure of the Poverello within a short time, nothing new of essential value has been added to what was already known of the saint. The energetic research work of recent years has resulted in the recovery of several important early texts, and has called forth many really fine critical studies dealing with the sources, but the most welcome feature of the modern interest in Franciscan origins has been the careful re-editing and translating of Francis’s own writings and of nearly all the contemporary manuscript authorities bearing on his life. Not a few of the controverted questions connected therewith are of considerable import, even to those not especially students of the Franciscan legend, but they could not be made intelligible within the limits of the present article. It must suffice, moreover, to indicate only some of the chief works on the life of St. Francis.
The writings of St. Francis have been published in “Opuscula S. P. Francisci Assisiensis” (Quaracchi, 1904); Böhmer, “Analekten zur Geschichte des Franciscus von Assisi” (Tübingen, 1904); U. d’Alençon, “Les Opuscules de S. François d’ Assise” (Paris, 1905); Robinson, “The Writings of St. Francis of Assisi” (Philadelphia, 1906).
(Catholic Encyclopedia)